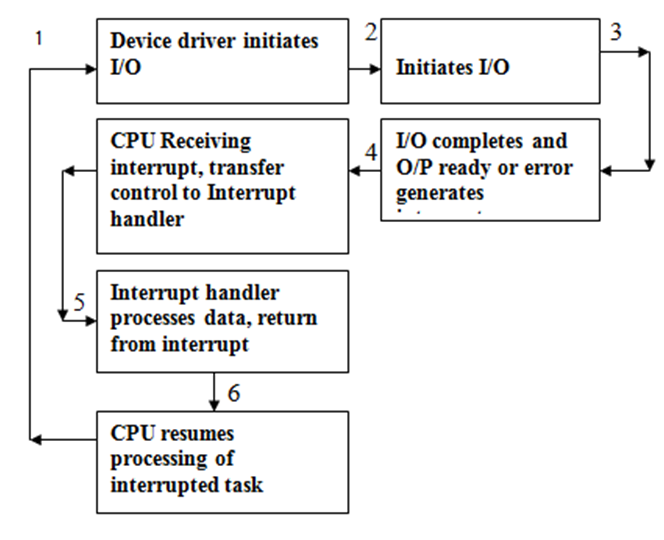
- The CPU hardware has a wire called Interrupt request line that CPU checks after executing every instruction.
- When the CPU detects that a device controller has pass a signal on interrupt request line, the CPU saves a small amount of state such as current value of instruction pointer and jumps to the interrupt handler routine at a fixed address in the memory.
- The interrupt handler performs necessary action and executes from interrupt instruction to return the CPU to the execution state prior to the interrupt.
- Each device has device controller. It sets interrupt request line 1 if that device generates interrupt.
- Most CPU has 2 interrupt request line.
(1) For Non – Markable interrupt which is reserved for events such as unrecoverable memory errors.
(2) For markable interrupt which is used by device controller to request service.
- The interrupt mechanism accepts an address; It is a number that selects a specific interrupt handling routine from a set.
- This address is an offset in the interrupt vector table. This vector table contains the memory address of interrupt handler.
- The interrupt mechanism also implements a system of interrupt priority levels.
- This mechanism enables the CPU to execute high priority interrupt by preempting the execution of low priority interrupt.
- A modern O/S interacts with interrupt mechanism in several ways.
- At the boot up time the OS checks the hardware buses to determine which devices are present and installs the corresponding interrupt handler addresses into the interrupt vector.
- During I/O, the various device controller raise interrupt, when they are ready for service.
- The interrupt mechanism is also used to handle a wide variety at exception such as divide by 0, accessing a protected or non existent memory address.
- A system call is a function call by an application program to invoke a kernel service.
- The system call checks the argument given by the application and executes a special instruction called S/W interrupt or trap.
- When the system call executes the trap instruction, the interrupt hardware saves the state of user mode, switches to kernel mode and executes the requested service.
- Interrupts are used throughout modern operating system to handle asynchronous events and trap to kernel mode routines in the kernel.
Interrupt driven I/O cycle.