- We can overload the binary operator just like the unary operators either using member function or friend function.
Overloading Binary Operator Using Member Function
- If we are using member function for overloading binary operator then we have to pass only one argument to the operator function.
- Consider the example given below of class ‘Box’ in which we are overloading operator ‘+’ to add the two objects of ‘Box’ class and create a new object which has sum of height and width of both previously created objects.
/* Program to overload binary operator + using member function */
#include "iostream.h"
#include "conio.h"
class Box
{
double width;
double height;
public :
Box() ; // default constructor
Box(double,double) ; // constructor with parameter
Box operator +(Box); // Overloading + operator
void show() ;
};
Box :: Box ()
{
width = height = 0.0 ;
}
Box :: Box (double w, double h)
{
width = w ;
height = h ;
}
// Operator function definition
Box Box :: operator +(Box b)
{
Box tmp; // create temporary object
tmp.height = height + b.height;
tmp.width = width + b.width;
return(tmp);
}
void Box :: show ()
{
cout<<"Width : "<<width <<endl ;
cout<<"Height : "<<height <<endl ;
}
void main()
{
Box b1,b2,b3;
b1 = Box(10,20) ;
b2 = Box(10,20) ;
b1.show() ; // show object 1
b2.show() ; // show object 2
// Call operator overload function + (This method is called by the object r1)
b3 = b1 + b2; // implicit call
b3.show(); // show object 3 after addition of both objects
}
- In above example we have overloaded ‘+’ operator using member function.
- We have to keep in mind the following points for the above example:
- An Operator function ‘operator +’ has one argument of type object of class ‘Box’.
- An Operator function returns the object of type ‘Box’.
- It is a member function of class ‘Box’.
- We have called the operator function by using the following statement:
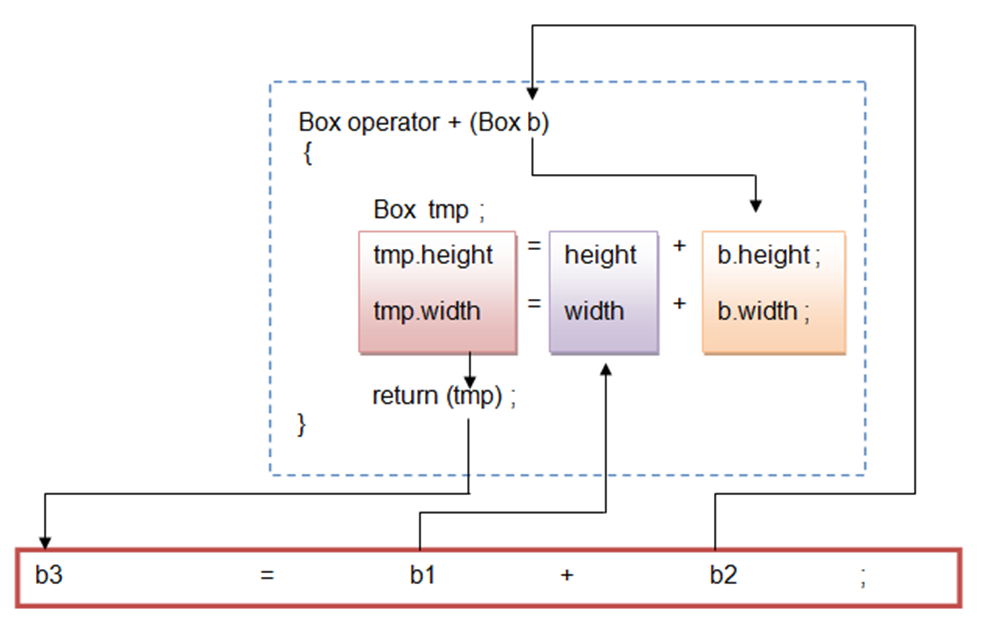
b3 = b1 + b2;
- Here object ‘b1’ calls the function ‘operator +’ and object ‘b2’ is passed as argument.
- The operator function returns the object and assigned to object ‘b3’.
b3 = b2 + b1 ;
- In above statement, object ‘b2’ calls the function ‘operator +’ and object ‘b1’ is passed as argument.
- In short, in operator overloading, left operator takes the responsibility to invoke the operator function and right operator is passed as an argument.
- We can also call the operator function by the following way.
b3 = b1.opeator + (b2); //calling like normal function. Explicit call
- The following is a graphical representation of what happens when operator overloading function is invoked.
Overloading Binary Operator Using Friend Function
- If we are using friend function to overload binary operator, we have to pass two arguments to operator function.
- Consider the previous example of class ‘Box’ in which we are overloading operator ‘+’ to add the two objects of ‘Box’ class and create a new object which has sum of height and width of both previously created objects.
- The same can be achieved for overloading binary operator “+” using friend function as below:
// Program to overload binary operator + using friend function
#include "iostream.h"
#include "conio.h"
class Box
{
double width;
double height;
public :
Box() ; // default constructor
Box(double,double) ; // constructor with parameter
friend Box operator +(Box, Box); // Overloading + operator
void show() ;
};
Box :: Box ()
{
width = height = 0.0 ;
}
Box :: Box (double w, double h)
{
width = w ;
height = h ;
}
// Operator function definition
Box operator +(Box b1, Box b2)
{
Box tmp; // create temporary object
tmp.height = b1.height + b2.height;
tmp.width = b1.width + b2.width;
return(tmp);
}
void Box :: show ()
{
cout<<"Width : "<<width <<endl ;
cout<<"Height : "<<height <<endl ;
}
void main()
{
Box b1,b2,b3;
b1 = Box(10,20) ;
b2 = Box(10,20) ;
b1.show() ; // show object 1
b2.show() ; // show object 2
// Call operator overload function + (This method is called by the object r1)
b3 = b1 + b2; // implicit call
b3.show(); // show object 3 after addition of both objects
}
- In above example we have overloaded ‘+’ operator using friend function.
- We have to keep in mind the following points for the above example:
- An Operator function ‘operator +’ has two arguments of type object of class ‘Box’.
- An Operator function returns the object of type ‘Box’.
- It is a friend function.
- We can call the operator function using the following statement:
b3 = b1 + b2; // implicit call using expression syntax
- Here we are implicitly calling operator function and passing two objects of class ‘Box’ as arguments. The operator function returns the object and assigned to object ‘b3’.
- We can also call the operator function explicitly by the following way.
b3 = operator + (b1, b2); // explicit call using normal function call

