- Every C program follows block structure.
- It is written as a collection of function also known as sub-routine.
- The basic structure of a C program is as follow:
[1] Documentation Section:
- This section contains information about the program such as author name, creation data & time etc.
- It provides guidelines to the program reader.
- It may also include logic of the program.
- This information is written as a comment.
[2] Link Section:
- It includes different library and header files that are required by the program.
- These header files are linked with the program during the linking steps.
- Some standard header files are <stdio.h>,<conio.h>, <string.h> etc.
[3] Definition Section:
- This section includes all the constant variables.
- They are defined with the “#define”
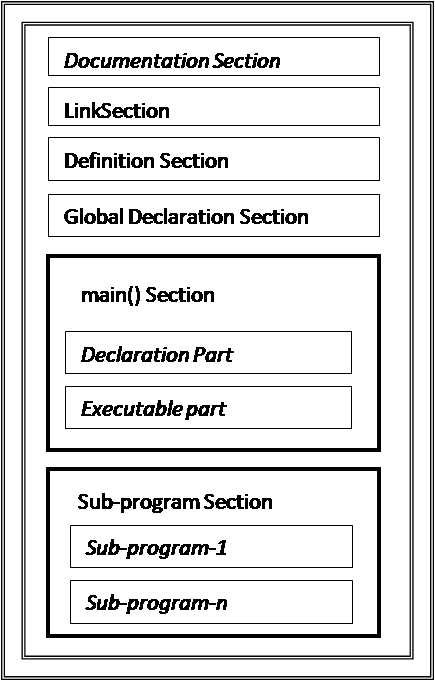 [4] Global Declaration Section:
[4] Global Declaration Section:
- All the global variables are defined in this section.
- Global variables can be accessed by any function of the program.
- Their scope is entire program.
[5] main() Section:
- The main()section is the main section of the C- program.
- Each C- program must have one and only one main function.
- It is define using main()
- Every statement of the C- program should be written in the main section.
- Opening ‘{‘specifies starting of the main function and closing ‘}’ specifies ending of the main function.
- main section is divided into the following two sections.
- Declaration part Executable part
- Declaration part contains all the local variables to be used in the main section.
- Executable section contains all the executable statement to perform the task.
[6] Sub-program Section:
- This section includes all the sub-program definitions.
- It is used when program is divided into different functions.
- Its order is not important; it can be place before or after the main section.Normally it is written after the main section.
